Sludge blanket measurement in wastewater treatment
Understanding sludge blanket measurement and its importance
In wastewater treatment, measuring the sludge blanket is a key parameter to guarantee the proper operation of settling processes. Whether in on-site sanitation systems or wastewater treatment plants (WWTP), controlling this parameter helps anticipate maintenance operations, prevent overflows and ensure regulatory compliance.

Definition of the sludge blanket
The sludge blanket corresponds to the transition zone between settled sludge and clarified water, visible in settling or pretreatment systems. This layer forms naturally over time under the effect of gravity and the organic load of wastewater.
Its height varies depending on flow rate, pollutant load and purge frequency.
If the sludge blanket rises too high, sludge may be carried over with the clarified water, degrading effluent quality and potentially causing regulatory non-compliance.
Measuring the sludge blanket indicates whether settling capacity is still sufficient or whether desludging or a purge is required.
Why monitor the sludge blanket?
Regular monitoring of sludge blanket height is essential to prevent upstream malfunctions.
Accurate measurement helps optimize operating costs by ensuring reasoned maintenance and sludge pumping, avoiding premature desludging and late interventions based on visual estimates.
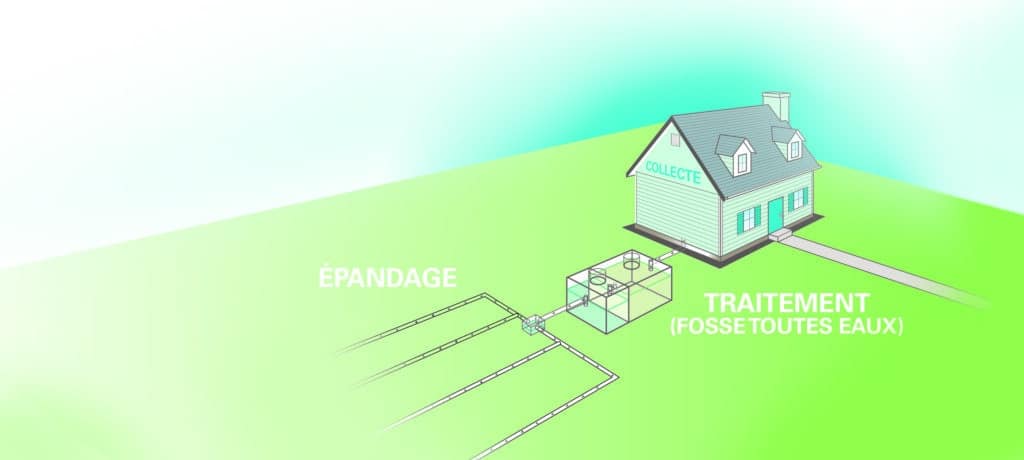
Sludge blanket measurement in on-site sanitation systems
Measuring the sludge blanket in an on-site sanitation system is essential to ensure its proper functioning and to plan desludging at the right time, before the system becomes saturated.
It prevents overflows and ensures compliance with regulations, which require desludging when sludge reaches 50% of the useful volume.
To perform this measurement, a sludge blanket detector (or sludge probe) is used to assess the thickness of sludge and floatables (grease, scum) in an all-waters tank or primary settler.
What exactly is the sludge blanket in an all-waters tank?
In an on-site sanitation system, the sludge blanket corresponds to the layer of settled solids accumulated at the bottom of the tank.
It is the lower zone where all materials heavier than water have deposited. Over time, this sludge compacts and undergoes anaerobic digestion (degradation by bacteria without oxygen).
Key issues of regular sludge blanket monitoring in on-site sanitation systems
- Avoid clogging of the system: when the sludge layer becomes too thick, it may be carried towards the treatment unit (sand filter, infiltration bed, microstation, etc.), causing clogging that can sometimes be irreversible.
- Ensure proper hydraulic functioning: an overloaded tank reduces available settling volume, compromising the separation between wastewater and solids.
- Preserve the lifespan of the installation: precise monitoring limits unnecessary interventions and avoids late desludging, often leading to failures or additional costs.
- Ensure regulatory compliance
Operating principle
Measurement devices operate according to different principles:
- Ultrasonic technology: the sensor emits a signal that detects differences in density between clear water, sludge and grease.
- Optical or differential pressure sensors: some instruments, such as Aqualabo’s NEON VB, assess reflectivity or conductivity of the layers.
These devices provide precise sludge height measurement, expressed in centimetres or as a percentage of total volume, without direct contact with the liquid.
Advantages compared with visual estimation
Method | Accuracy | Safety | Speed | Compliance |
Visual estimation (stick, rod, etc.) | Low | Contact risk | Slow | Not guaranteed |
Sludge blanket detection device | High | No direct contact | Fast | Compliant |
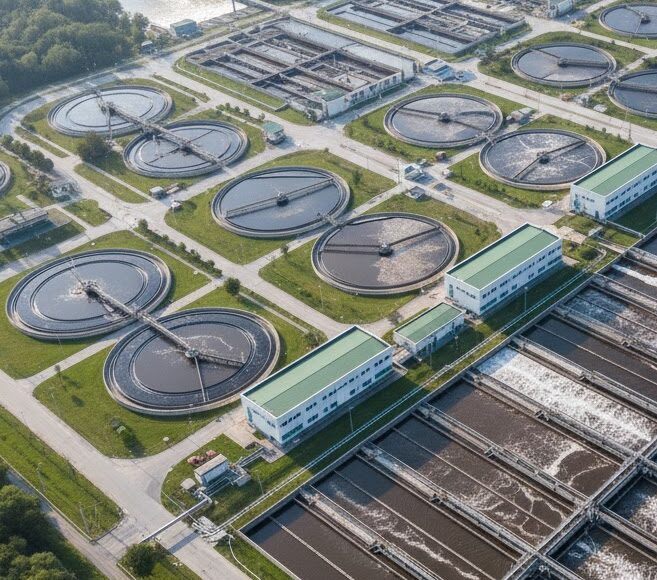
Sludge blanket measurement in wastewater treatment plants (WWTP)
Sludge blanket measurement is also used in wastewater treatment plants to determine the height of the separation zone between settled sludge and clarified water in primary or secondary settling tanks.
This information is essential to adjust purges, monitor basin load and avoid solids loss in the final effluent.
Automated sludge blanket monitoring helps optimize purge operations, prevent suspended solids loss and ensure stable, controlled operation.

Why is sludge blanket measurement essential?
- Maintain treatment performance: an excessively high sludge blanket causes solids to escape toward the clarifier or discharge, deteriorating treated water quality.
- Optimize sludge management: measurement helps define optimal purge frequency, limiting overspending from excessive purges and overflow risks from delayed purges.
- Prevent malfunctions: monitoring sludge level highlights hydraulic imbalances, foaming phenomena or abnormal flotation.
- Strengthen safety and traceability: automatic sensors ensure reliable measurements without direct contact and continuously record operating data.
Operating principle of sludge blanket detectors in WWTPs
In wastewater treatment plants, instruments mainly use two technologies:
- Ultrasonic density variation detection between clear water and settled sludge
- Optical or differential pressure sensors, depending on the integrated technology
They transmit continuous measurements of sludge blanket height, in centimetres or as filling percentage, displayed on-screen or directly on the supervisory system.
Advantages compared with manual measurement
Method | Accuracy | Safety | Continuous monitoring | Traceability |
Manual measurement (rod, gauge) | Low | Exposure risk | Occasional | Not guaranteed |
Sludge blanket detection device | High | No direct contact | Continuous | Recorded |
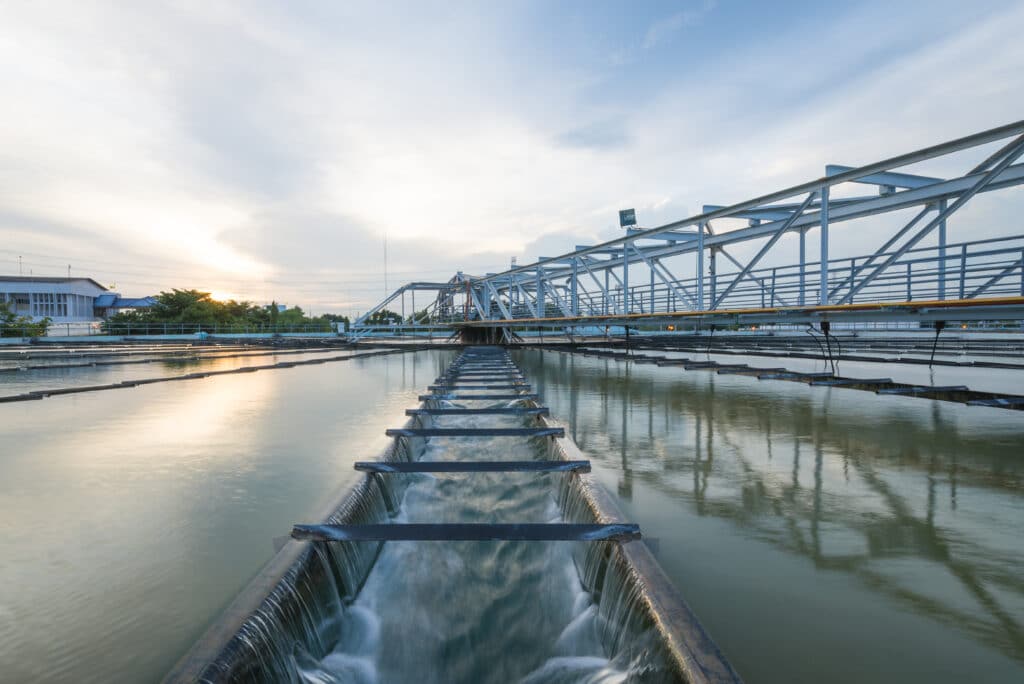
How to measure the sludge blanket without interrupting operation?
Automatic sensors installed in basins continuously measure sludge blanket height without manual intervention.
Thanks to ultrasonic or optical technology, devices transmit real-time data to the supervisory system.
This continuous monitoring ensures measurement traceability and enables rapid detection of deviations, without interrupting basin operation.
What measurement frequency is required for reliable monitoring?
The required measurement frequency depends on the type of installation.
In wastewater treatment plants, continuous monitoring using automatic sensors is recommended to ensure process stability.
These devices transmit real-time data, allowing operators to immediately adjust purges or recycling flow.
What are the risks of poor monitoring?
Insufficient or irregular monitoring can quickly compromise plant performance.
If the sludge level exceeds the settling zone, sludge may be carried over to the clarifier or final effluent, increasing suspended solids and leading to non-compliant discharge.
Conversely, purging too frequently disrupts active biomass and reduces biological treatment efficiency.

Our AQUALABO solutions
Aqualabo offers several instruments suitable for sludge blanket measurement in on-site sanitation systems and wastewater treatment plants (WWTP).
These devices stand out for their precision, reliability and compatibility with various measurement environments.
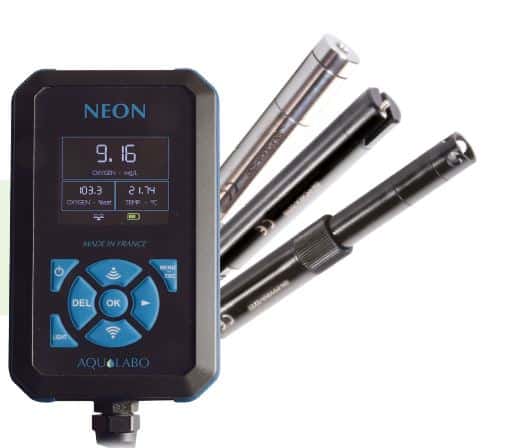
Handheld Sludge blanket detection -NEON VB
Designed for fast and versatile use, the Aqualabo NEON Sludge Blanket Detection is a portable device ideal for monitoring sludge levels in both on-site sanitation and WWTP applications.
Compact and intuitive, it accurately measures sludge blanket height and medium temperature.
Its logging capacity (up to 30,000 points) and Wi-Fi transfer facilitate field data collection and analysis, with no cables or complex installation.
It enables precise localisation of sludge level in septic tanks and assessment of tank filling rate, ensuring optimal maintenance of on-site sanitation systems.
It is also used in urban wastewater treatment to measure sludge blanket level in primary and final clarifiers.
Finally, it is suitable for industrial effluent treatment, ensuring reliable monitoring of sludge level in primary and secondary settling basins.

VB5 Sensor
The VB5 sensor accurately measures sludge blanket level using optical technology combined with high-performance digital processing.
Available in portable or fixed versions, it is suitable for on-site sanitation and WWTP installations and provides automated, reliable and continuous monitoring of settling tanks.
ODEON Portable Range
The ODEON range offers a complete solution for water quality monitoring and physico-chemical parameter measurement.
This multiparameter portable instrument can accommodate several DIGISENS digital sensors, including a sensor dedicated to sludge blanket measurement.
It supports multiparameter field monitoring both in WWTP and on-site sanitation systems, offering a comprehensive view of treatment performance.
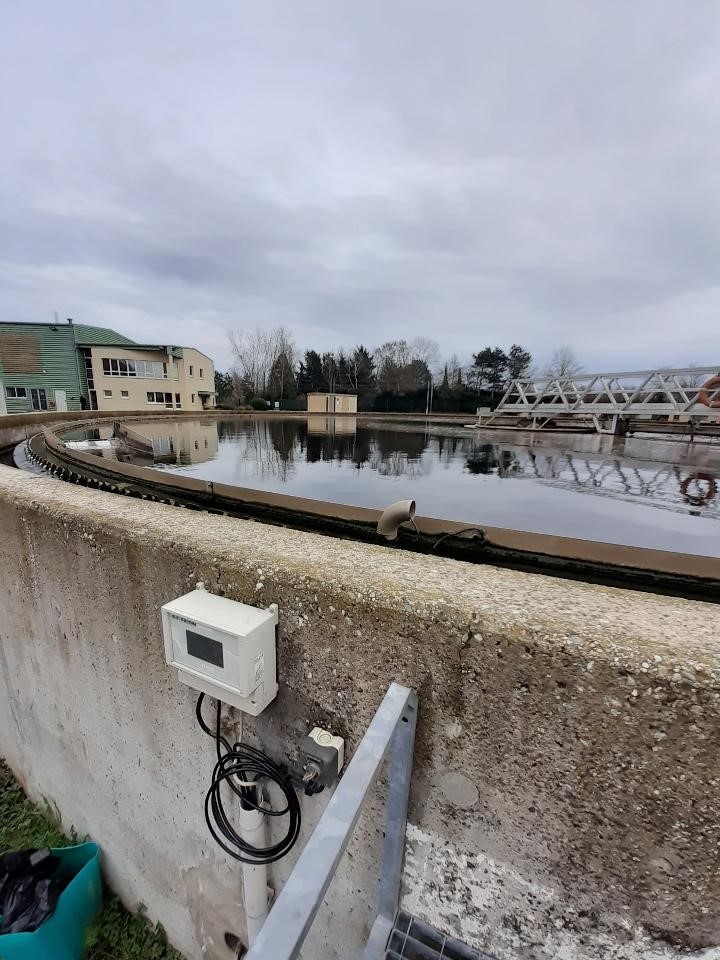
ACTEON Fixed Range
Highly versatile and equipped with an intuitive touchscreen, the Aqualabo ACTEON 5000 is a multiparameter instrument capable of measuring many indicators, including the sludge blanket.
Its robust design and advanced functionalities make it a true supervision centre, ensuring complete and real-time monitoring of key water treatment parameters.

Towards controlled sludge blanket management
Whether in on-site sanitation or wastewater treatment plants (WWTP), sludge blanket measurement is essential to maintain treatment performance and reliability.
Regular and automated measurement preserves effluent quality while optimising operating costs.
To discover the most suitable instruments for your needs, explore Aqualabo’s solutions or contact our teams for personalised support.




